Paradigm CTF 2021
Paradigm CTF 2021代码库
完整wp代码仓库
HELLO 送分题,调用solve即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 const { expect } = require("chai");
SECURE 这句是将setup中的WETH转走,此时balance为0
1 wallet.execModule(tokenModule, abi.encodeWithSelector(TokenModule(0x00).deposit.selector, WETH, address(this), msg.value));
如果Setup合约有 50 (W)ETH,挑战就解决了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 const { expect } = require("chai");
BABYCRYPTO 通关要求是验签成功
1 2 3 4 5 if not pub.verifies(test, ecdsa.Signature(r, s)):print ("better luck next time" )1 )print (flag)
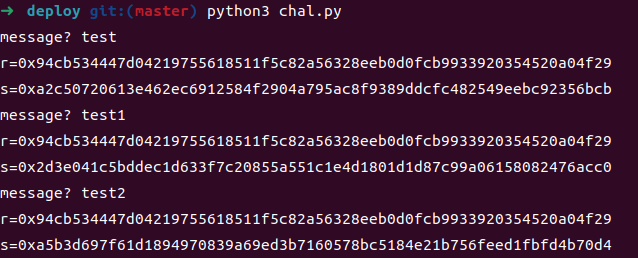
可以发现每一次的r都是相同的
由此可以联想到[capture the ether —— Account Takeover](https://sissice.github.io/2022/04/02/capture the ether wp/)
我们可以利用两个相同的r计算出私钥,再利用私钥对消息进行签名,最后解析出签名中的r和s即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 from random import SystemRandomfrom ecdsa import ecdsaimport sha3import binasciifrom typing import Tuple import uuidimport osimport mathdef hash_message (msg: str ) -> int :""" hash the message using keccak256, truncate if necessary """ "utf8" ))int (binascii.hexlify(d), 16 )or 1 len (d)max (0 , dlen - olen)return ndef modInverse (b,m ):if (g != 1 ):return -1 else :return pow (b, m - 2 , m)def modDivide (a,b,m ):if (inv == -1 ):print ("Division not defined" )else :return (inv*a) % mif __name__ == "__main__" :input ("msg1? " )input ("msg2? " )int (input ("r1? " ), 16 )int (input ("s1? " ), 16 )int (input ("s2? " ), 16 )int (input ("test? " ), 16 )print (f"solved r=0x{sig.r:032x} " )print (f"solved s=0x{sig.s:032x} " )
BROKER 完成挑战的条件是合约broker持有的weth少于5 ether
1 2 3 function isSolved() public view returns (bool) {
而Broker 中的初始余额为 25 WETH 和 500,000 Token
broker中可以转出WETH的函数有两个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 function withdraw(uint256 amount) public {
其中withdraw需要满足safeDebt(msg.sender) >= debt[msg.sender]
liquidate需要满足safeDebt(user) <= debt[user]
safeDebt 由 deposited[user] 和 rate() 决定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function rate() public view returns (uint256) {
broker是一家超额抵押贷款银行。以 WETH 作为抵押,提供 Token 作为借贷。当抵押品被认为抵押不足时,该账户可以被清算。正如我们之前提到的,抵押因子将根据 Uniswap 交易对的价格来决定。
攻击思路(生产环境没有足够多的ETH,中可以在一个闪贷中完成攻击):
Deposit WETH 作为抵押品。尽可能多的“借”Token,让清算更容易。
在 Uniswap 交易对中购买 Token,提升 Token 价格。
由于 Token 价格上涨,我们使用的账户抵押不足。
清算账户,偿还适当数量的Token以提取Broker中的WETH。
Uniswap V2 中的swap
UniswapV2Router02.sol
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 pragma solidity 0.8.0;
FARMER 要求是Dai的余额小于期望值,且farmer和faucet的COMP余额都为0.
1 2 3 4 5 function isSolved() public view returns (bool) {
期望值expectedBalance的定义
1 expectedBalance = DAI.balanceOf(address(farmer)) + farmer.peekYield();
peekYield其实质是Uniswap中,COMP->WETH->DAI的连续两次swap。我们直到SWAP的价格曲线是在 x*y=k 的曲线上移动,故一个简单的思路是在让曲线上的点先向下移动,再进行COMP->WETH->DAI的交换,此时能够换到的DAI的数量就会比peekYield的数量少。即三明治攻击
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 function peekYield() public view returns (uint256) {
recycle也是进行COMP->WETH->DAI的交换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function recycle() public returns (uint256) {
所以有以下攻击合约
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
YIELD_AGGREGATOR 目标是weth余额清零
1 2 3 4 function isSolved() public view returns (bool) {
解法一 这里的 transferFrom 是一个外部调用,可以利用外部调用实现重入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function deposit(Protocol protocol, address[] memory tokens, uint256[] memory amounts) public {
deposit 中不会检查输入的protocol和tokens,并且使用balanceBefore和balanceAfter这种快照模式来计算用户存入金额
利用transferFrom重入有以下流程
deposit fakeToken,数目不限
balanceUnderlying = 50 (setup后的初始值)
fakeToken.transferFrom (已重写)
deposit weth 50
weth.transferFrom 50
balanceUnderlying = 100
diff = 50
poolTokens += diff (第一次)
balanceUnderlying = 100
diff = 50
poolTokens += diff (第二次)
demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 contract yieldExploit {
解法二 自己生成一个新的bank,deposit weth 50,增加poolTokens[attackContract]的值,再withdraw 原bank 50
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 contract ExploitYieldAggregator {
BOUNCER 要求是清空合约bouncer的余额,初始状态下bouncer余额为50+2 ETH
1 2 3 function isSolved() public view returns (bool) {
只有payout具有transfer功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 function payout(ERC20Like token, address to, uint256 amount) private {
payout被redeem调用
1 2 3 4 function redeem(ERC20Like token, uint256 amount) public {
所以首先要使 tokens[msg.sender][address(token)] 被增加
convert可以达成需求,但是会在proofOfOwnership中检查msg.value == amount
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function convert(address who, uint256 id) payable public {Entry memory entry = entries[who][id]require (block.timestamp != entry .timestamp, "err/wait after entering" )if (address(entry .token) != ETH) {require (entry .token.allowance(who, address(this)) == type(uint256).max, "err/must give full approval" )require (msg.sender == who || msg.sender == delegates[who])entry .token, who, entry .amount)entry .token)] += entry .amount
所以选择利用convertMany,支付1份value而使 tokens[who][address(entry.token)] n倍的增加
1 2 3 4 5 function convertMany(address who, uint256[] memory ids) payable public {
demo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
BABYSANDBOX 要求部署的BabySandbox合约的代码大小变为 0 ,即销毁他
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 function isSolved() public view returns (bool) {
staticcall 意思是等同于CALL ,除了它不允许任何状态修改指令。因此 SELFDESTRUCT 不允许在 staticcall 期间使用
BabySandbox.run()的内部逻辑
首先会判断msg.sender == address(this),即判断是否为合约自身调用。由于我们将会外部调用该合约,故此时的msg.sender是code合约地址,判断为否。
然后进入staticcall(address(this))部分,它重进入自己的合约内,再次调用babysandbox.run(code)方法。
1 2 3 if iszero(staticcall(0x4000, address(), 0, calldatasize(), 0, 0)) {
此时需注意,由于是重进入,故此时的msg.sender与address(this)相等。故经过判定,会进入到delegatecall(code)的逻辑中。
staticcall(address(this))通过后,会进入call(address(this))调用,同样的参数,同样的逻辑过程。
1 switch call(0x4000, address(), 0, 0, calldatasize(), 0, 0)
重进入自己的合约内,再次调用babysandbox.run(code)方法,进入到delegatecall(code)的逻辑中
在delegatecall(code)逻辑中,调用外部合约code的fallback()方法
因此此时需要在code.fallback()函数中,不直接返回,而是执行selfdestruct(tx.origin)来销毁babysandbox合约。
注意,由于delegatecall 不会改变上下文,所以msg.sender和tx.origin都可以使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import "./Setup.sol";